Self-localized states in magnetoordered systems
A special type of condensed medium is the medium with magnetic order. Hamiltonian of the interaction between an electron and the magnetoordered crystal has the form
| (4.1) | 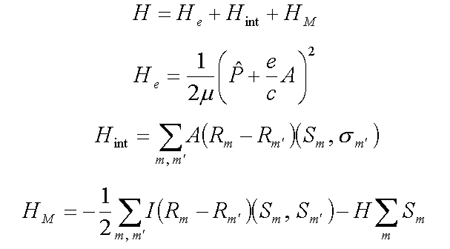 |
where Hint and HM – are s-d(f) exchange and Heisenberg Hamiltonians, respectively. It is shown in /7/ and /8/ that as distinct from the polaron in the ionic crystal, the electron interacts with magnetic atom spins at a short range and electron self-localized states are separated from delocalized ones by a potential barrier. The electron capture would thus be expected to be of activation character ехр(-А/КТ). In /11/ new types of electron localized states separated from each other by a potential barrier were found in antiferromagnetics with coulomb impurity. It was shown, that under the influence of an external magnetic field the electron may change from one state into the other. These results can be used in explaining conductive properties of magnetic semiconductors.
In /7/ and /10/ a new type of self-localized states in antiferromagnetics in a quantizing magnetic field is found, such that a particle can transfer into these states without overcoming the potential barrier. These are self-consistent states of an electron and a soliton-type magnetization distribution (Fig.1), extended in shape along the magnetic field direction. These states are responsible for optical and electric properties of antiferromagnetic semiconductors in a strong magnetic field. They may also be vital in oxide ceramics, where the high-temperature superconductive phase coexists with the antiferromagnetic one.
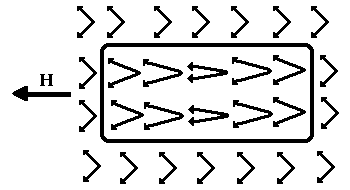
in antiferromagnetic without overcoming a potential barrier