Long-range electron transfer in proteins
Review of the studies carried out
The problem of long-range electron transfer in biological systems is intensively studied in molecular biology both experimentally and theoretically with regard, for example, to the electron transfer in the reaction center of photosynthesis, respiratory chain of electron transport, etc.
The work at this problem was started at our Institute in the late 80▓s. In the papers /6/, /14/, /19/ the problem of long-range electron transfer is treated using the model of self-consistent electron extended states in proteins. According to this approach, the whole of the biomacromolecule takes part in the formation of self-consistent states. The spectroscopic experiments with metal containing heme proteins are accounted for by the properties of heme wave functions of the electron, while the electron transfer is explained by the characteristics of self-consistent extended states.
At the present time this physical theory yields correct values for the protein reorganization energy and the dependence of the transfer rate on the distance between the reaction centers in protein self-exchange reactions.
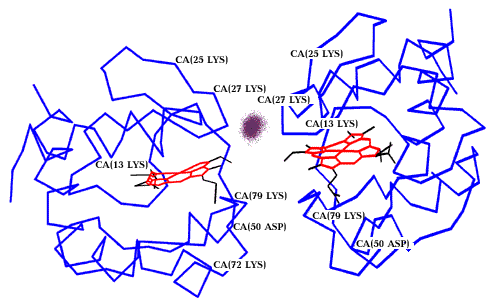
Figure shows the scheme of a self-exchange reaction in the complex cytc/cytc through an intermediate excited state (in the center):